Can Adware Harm Your PC? Complete Guide to Adware Threats & Protection
Learn how adware harms your PC, including performance degradation, privacy risks, and security vulnerabilities. Discover detection methods and removal strategie...
Understand what adware is, how it operates in marketing, how to identify and manage it, and the legal and ethical considerations surrounding this type of software.
An adware is a software, that supports and provides advertisements. These advertisements are the source of revenues for their author.
Adware software is often downloaded together with different programs and people usually do not realize it. It is automatically included in the installation. An Adware software can also be known as malware or spyware, because it collects information about the user and then shows undesired advertisements.
Adware operates by embedding itself in software applications or exploiting vulnerabilities in a device’s operating system. Once installed, it serves advertisements directly within the application or through separate pop-ups. The creators of adware profit through various models such as pay-per-click (PPC), pay-per-view (PPV), and pay-per-install (PPI). Additionally, adware can collect data on users’ browsing habits and locations to tailor advertisements and sell this information to third parties, raising privacy concerns.
Adware can be categorized based on its execution and user consent:
Adware is not confined to personal computers; it also affects mobile devices, especially those running Android operating systems. Mobile adware often embeds itself within apps downloaded from third-party app stores, potentially leading to relentless ads, data collection, or unauthorized subscriptions to premium services.
While adware is often classified under the broader category of malware due to its intrusive nature, not all adware is harmful. The distinction lies in user consent and the presence of malicious intent. Malware includes a wide range of malicious software such as spyware, viruses, and ransomware, whereas adware primarily focuses on generating advertising revenue.
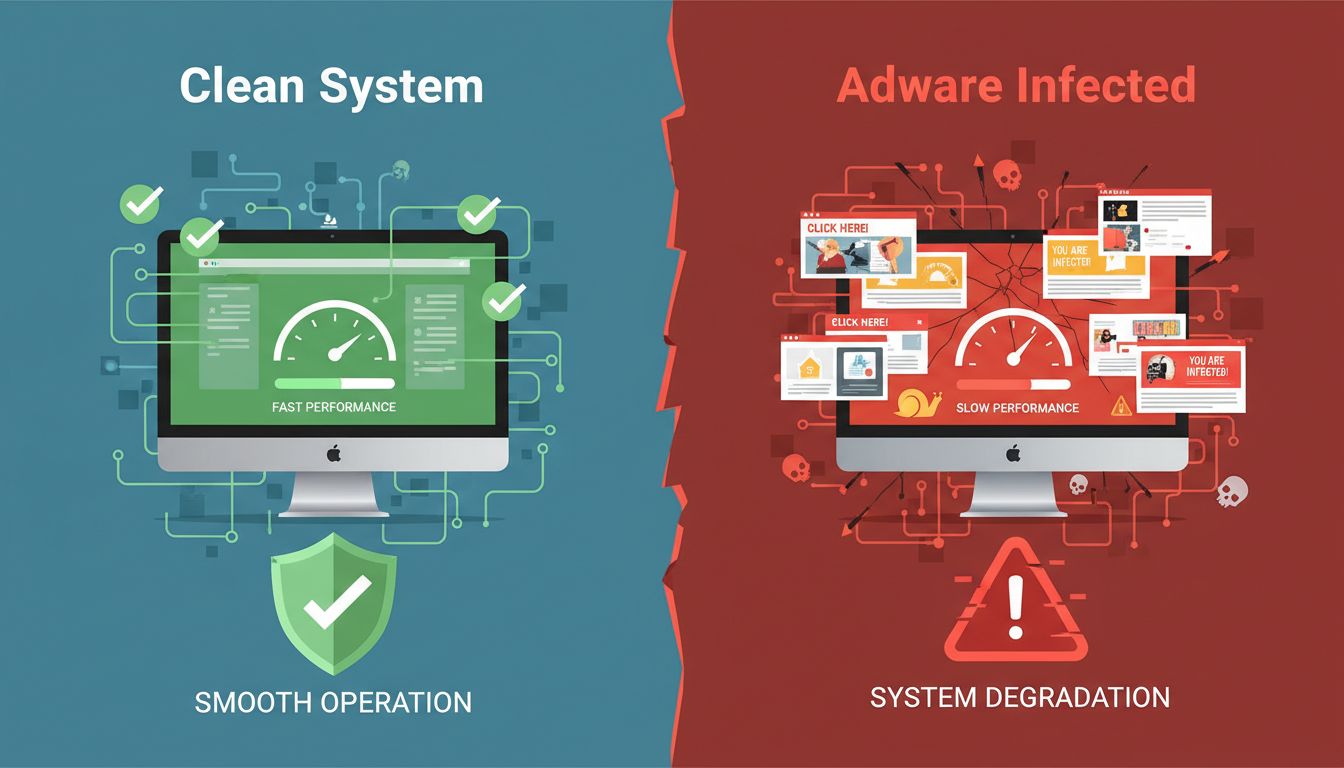
Detecting adware is often straightforward due to its disruptive nature. Common symptoms include:
On mobile devices, signs of adware include:
Removing adware involves several steps, depending on the severity of the infection:
Prevention is the most effective strategy against adware. Best practices include:
The legality of adware largely depends on user consent and the transparency of its installation. While legitimate adware respects privacy and provides users with an option to opt-out, malicious adware violates privacy laws and is often used for fraudulent purposes. Many jurisdictions have enacted laws to combat illegal adware practices, emphasizing the importance of user consent and data protection.
Adware is a type of malware that displays unwanted advertisements on a user’s computer. These ads often appear in the form of pop-ups or pop-unders.
Adware can potentially harm your computer by installing itself without your knowledge and slowing down your computer's performance.
Adware is a type of software that automatically displays or downloads advertising material when a user accesses the internet.
Learn how to identify, remove, and prevent adware to keep your devices and data secure.

Learn how adware harms your PC, including performance degradation, privacy risks, and security vulnerabilities. Discover detection methods and removal strategie...
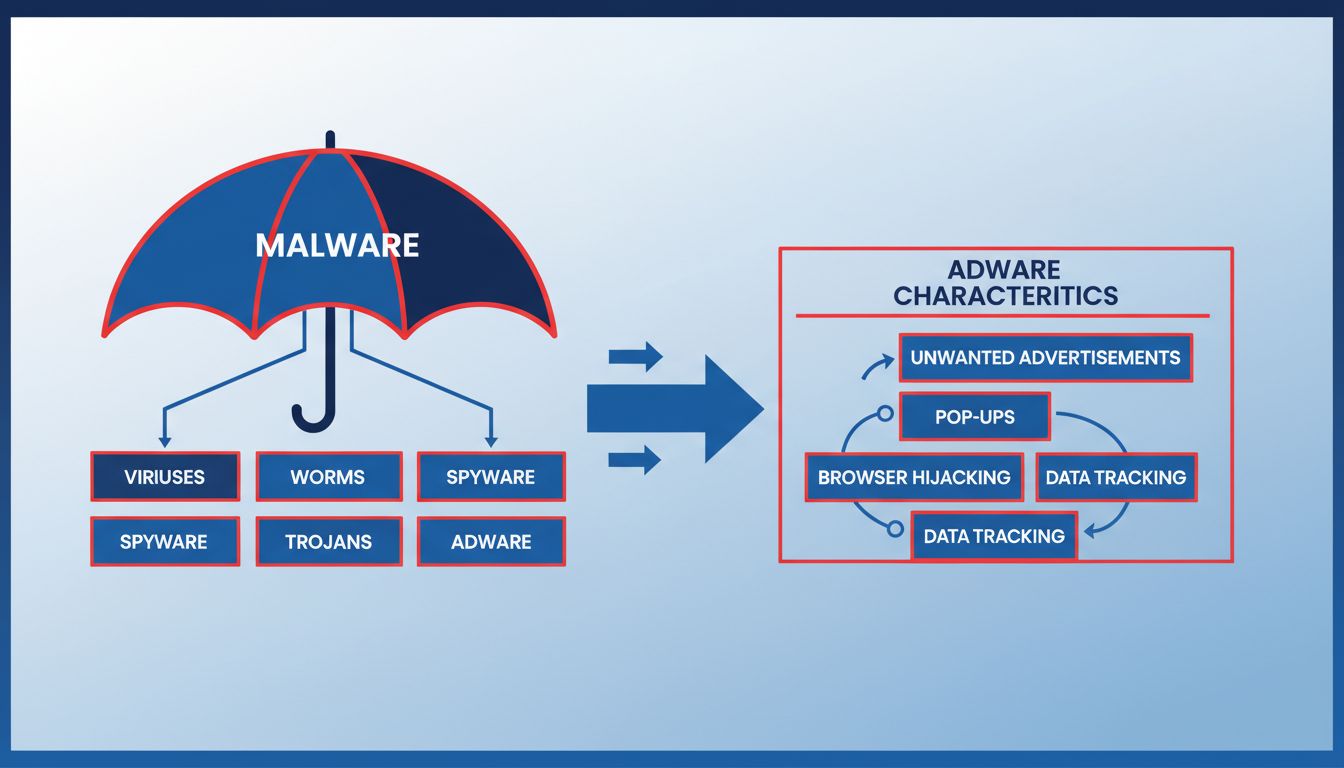
Learn whether adware is malware, how they differ, and why adware poses security risks. Comprehensive guide to protecting your devices from unwanted software.
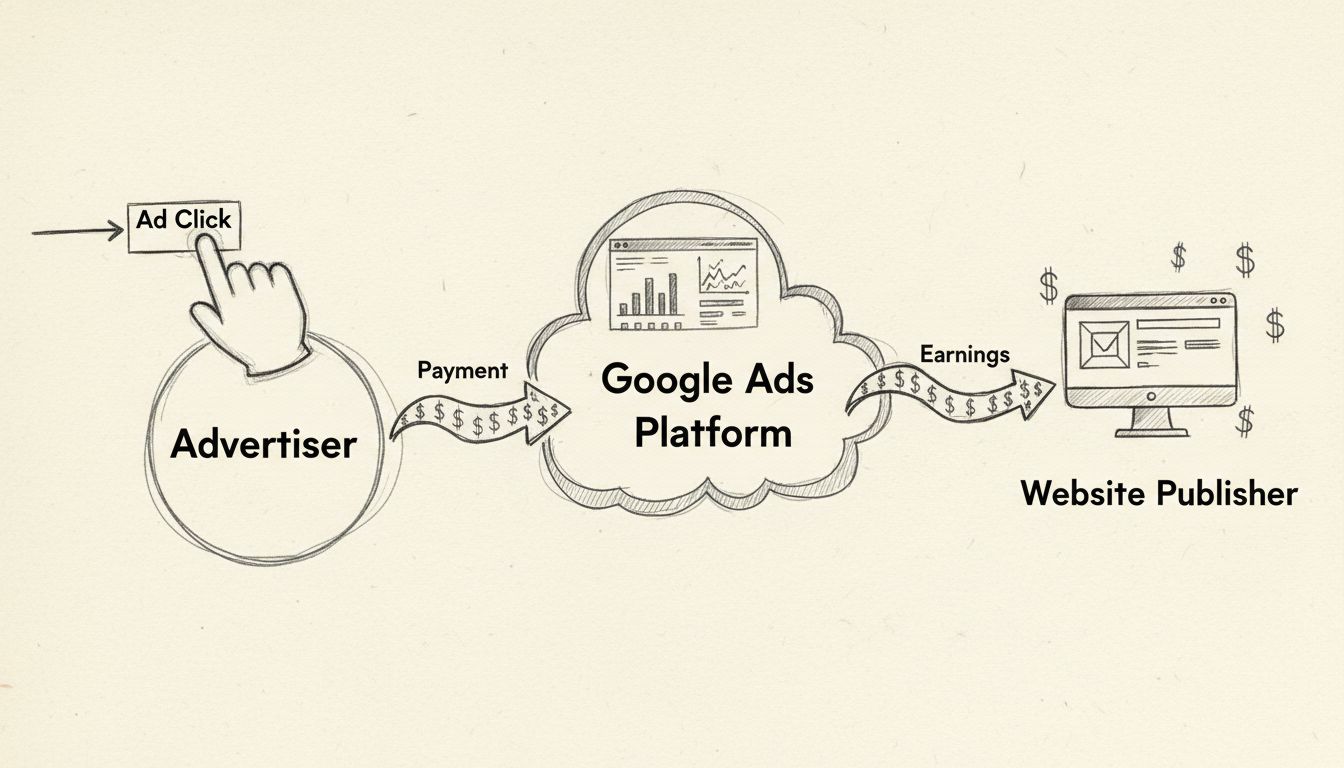
Learn how to earn money from pay-per-click advertising. Discover PPC strategies, platforms, and proven methods to monetize your website with PostAffiliatePro.
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.