What is Positive Pay? Complete Guide to Check Fraud Prevention
Learn what Positive Pay is and how this automated cash management service prevents check fraud. Discover how it works, benefits, costs, and best practices for b...
Positive Pay is a fraud prevention service used by financial institutions to verify checks and protect businesses from unauthorized transactions.
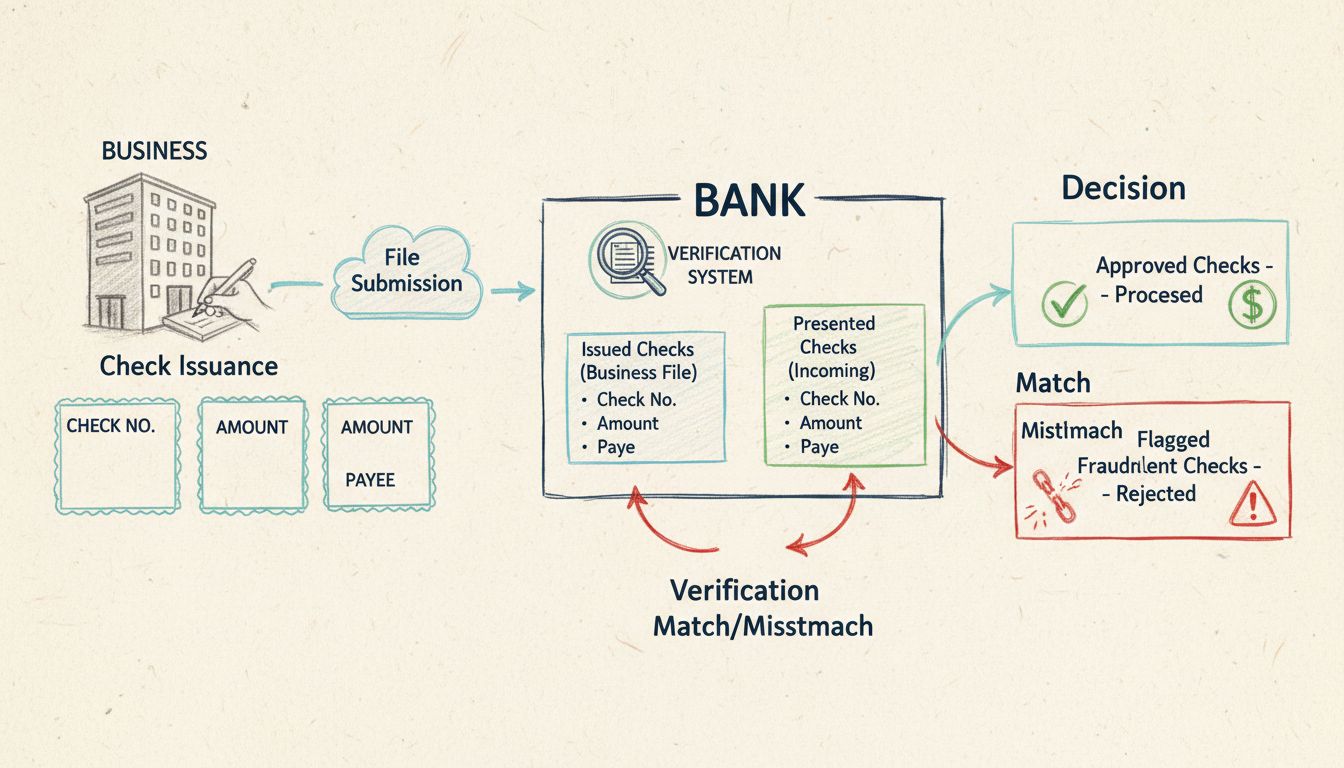
Positive Pay is essentially an automated cash management service meticulously crafted to sniff out and prevent check fraud by verifying checks presented for payment against a compiled list of checks issued by a business. This verification sequence involves a cross-examination of essential check details like check number, monetary amount, and account number. Any incongruences are quickly flagged for further scrutiny, permitting the business to either sanction or decline the payment. By doing so, this system acts as a bulwark against financial losses and liabilities, granting businesses an extra shield of security in their financial dealings.

Positive Pay functions through an orchestrated series of systematic processes ensuring only authorized checks see successful processing. Here’s a step-by-step walkthrough:
This precise process ensures only legitimate checks pass through, acting as a defense line against fraudulent encroachments.
Positive Pay isn’t a monolith; it presents various forms tailored to meet specific fraud prevention exigencies:
The deployment of Positive Pay yields manifold advantages to businesses:
Bringing Positive Pay into play necessitates a concerted endeavor between businesses and their banking partners:
In affiliate marketing and accompanying software domains, Positive Pay has a notable role in preserving financial integrity. By securing financial transactions, businesses can guarantee that affiliate payouts and other financial interactions stay safe from fraud. Implementing Positive Pay can also enhance trust within affiliate networks, assuring affiliates of the security and legitimacy of their commissions and payments.
Positive Pay is an automated cash management service that prevents check fraud by verifying checks presented for payment against a list of checks issued by a business.
Positive Pay works by requiring businesses to submit a list of issued checks to their bank. When a check is presented for payment, the bank verifies its details against this list and flags any discrepancies for review.
Types include Standard Positive Pay, Payee Positive Pay, Reverse Positive Pay, and ACH Positive Pay, each catering to different verification needs and transaction types.
Benefits include significant fraud prevention, increased financial control, reduced losses from fraudulent checks, simplified reconciliation, and greater stakeholder confidence.
Unlock the language of affiliate marketing and master key terms to succeed in your efforts.

Learn what Positive Pay is and how this automated cash management service prevents check fraud. Discover how it works, benefits, costs, and best practices for b...
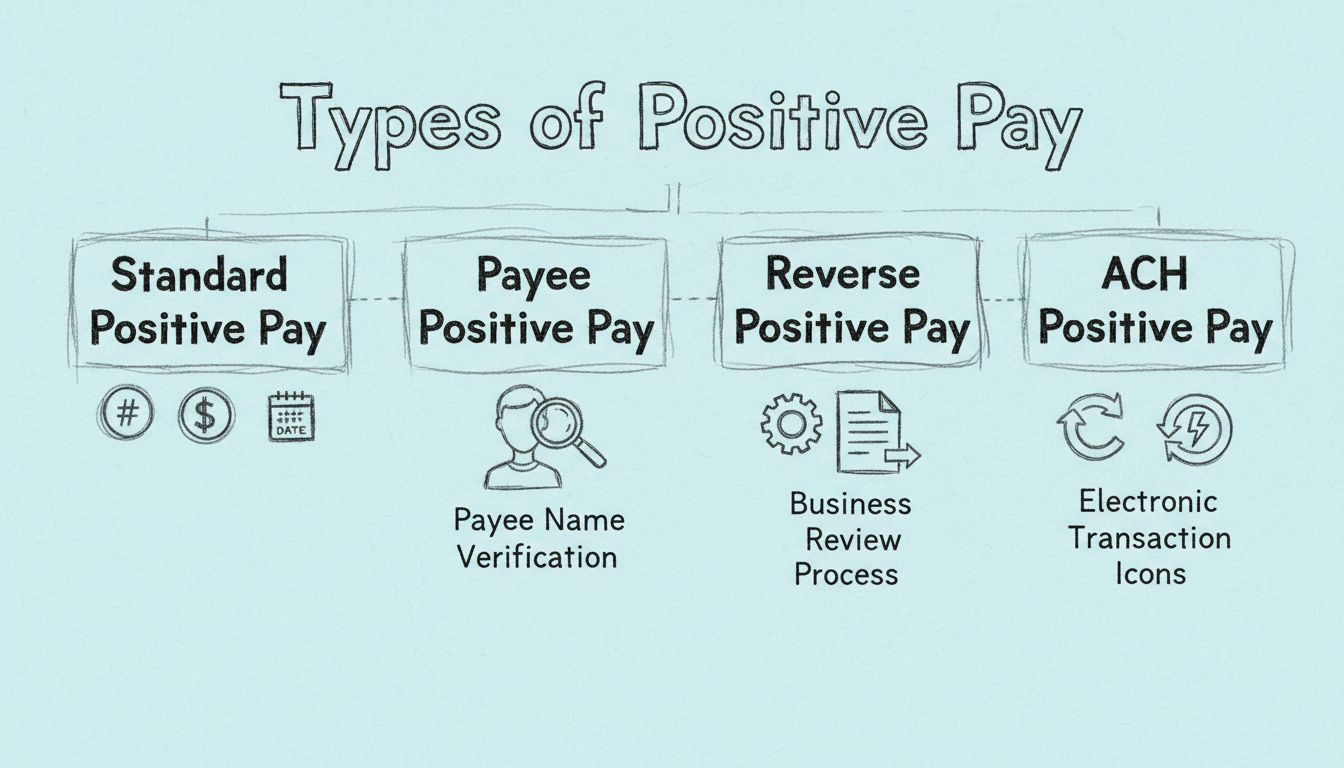
Comprehensive guide to the four types of Positive Pay systems: Standard, Payee, Reverse, and ACH Positive Pay. Learn how each protects against check and electro...
Pay per sale (PPS) is a performance-based affiliate marketing model where advertisers reward affiliates for each sale generated through their promotional effort...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.